RAM
RAM also known as random access memory. It is much faster to read from and write to than the other in a computer, the hard disk, floppy disk, and CD-ROM. The data in RAM stays there only as long as your computer is running and RAM is the most common type of memory found in computers.
Cache Memory
A cache memory is random access memory (RAM) that a computer microprocessor can access more quickly than it can access regular RAM. The cache memory is a more smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations.
ROM
ROM stands for read-only-memory, it is "built-in" computer memory containing data that normally can only be read, not written to. ROM contains the programming that allows your computer to be "booted up" or regenerated each time you turn it on. It sustained by a small long-life battery in your computer.
Flash Memory
Flash memory is a type of electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM). It often used in USB removable storage devices and MP3 players. On the other hand, flash memory is not useful as random access memory which is RAM because RAM needs to be addressable at the byte level.
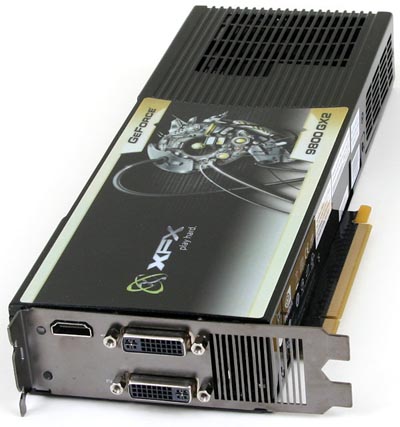
Graphic Card
Graphic card is a device installed in a computer which consists of a graphics processing unit designed to help process and display images, especially 3D graphics. It is an expansion card whose function is to generate and output images to a display.
Sound Card
A sound card is also known as an audio card. It is an expansion board that enables a computer to manipulate and output sounds. Sound cards are necessary for nearly all CD-ROMs and have become commonplace on modern personal computers and allow the computer to play digital audio or musical instrument sounds.
Network Interface Card
NIC stands for Network Interface Card, is a computer circuit board or card that is installed in a computer so that it can be connected to a network. Most NICs are designed for a particular type of network, protocol and media, although some can serve multiple networks.
Plug and Play
In computing, plug and play refers to the ability of a computer system to automatically configure expansion boards and other devices. Instead the computer automatically recognizes the device, load news drivers for the hardware if needed and begins to work with the newly connected device.
Serial Port
A serial port is a type of connection on PCs that used for peripherals such as mice, gaming controllers, modems and older printers. It is a port or interface that can be used for serial communication, in which only 1 bit is transmitted at a time.
Parallel Port
A parallel port is also known as a printer port or Centronics port, for connecting an external device such as a printer. Most personal computers have both a parallel port and at least one serial port. On PCs, the parallel port uses a 25-pin connector and is used to connect printers, computers and other devices that need relatively high bandwidth.
Universal Serial Bus Port
USB shorts for Universal Serial Bus, a common interface that enables communication between devices and a host controller such as a personal computer. It can be used to connect keyboards, mice, game controllers, printers, scanners, digital cameras and removable media drivers, just to name a few. USB also supports Plug and Play installation and hot plugging.
Firewire Port
The Firewire port is the high-speed interface has become a hot new standard for connecting peripherals, which can be used to connect some devices such as digital video cameras, hard drives, audio interfaces and MP3 players. A standard Firewire connection can transfer data at 400Mbps, which is roughly 30 times faster than USB 1.1.
Ethernet Port
Ethernet is the most widely-installed local area network (LAN) technology. It defines a number of wiring and signaling which standards for the Physical Layer of the standard networking model as well as a common addressing format and a variety of Medium Access Control procedures at the lower part of the Data Link Layer.
High Definition Multimedia Interface
HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) is a compact audio or video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. A significant difference between HDMI and DVI is that HDMI supports audio as well as video.